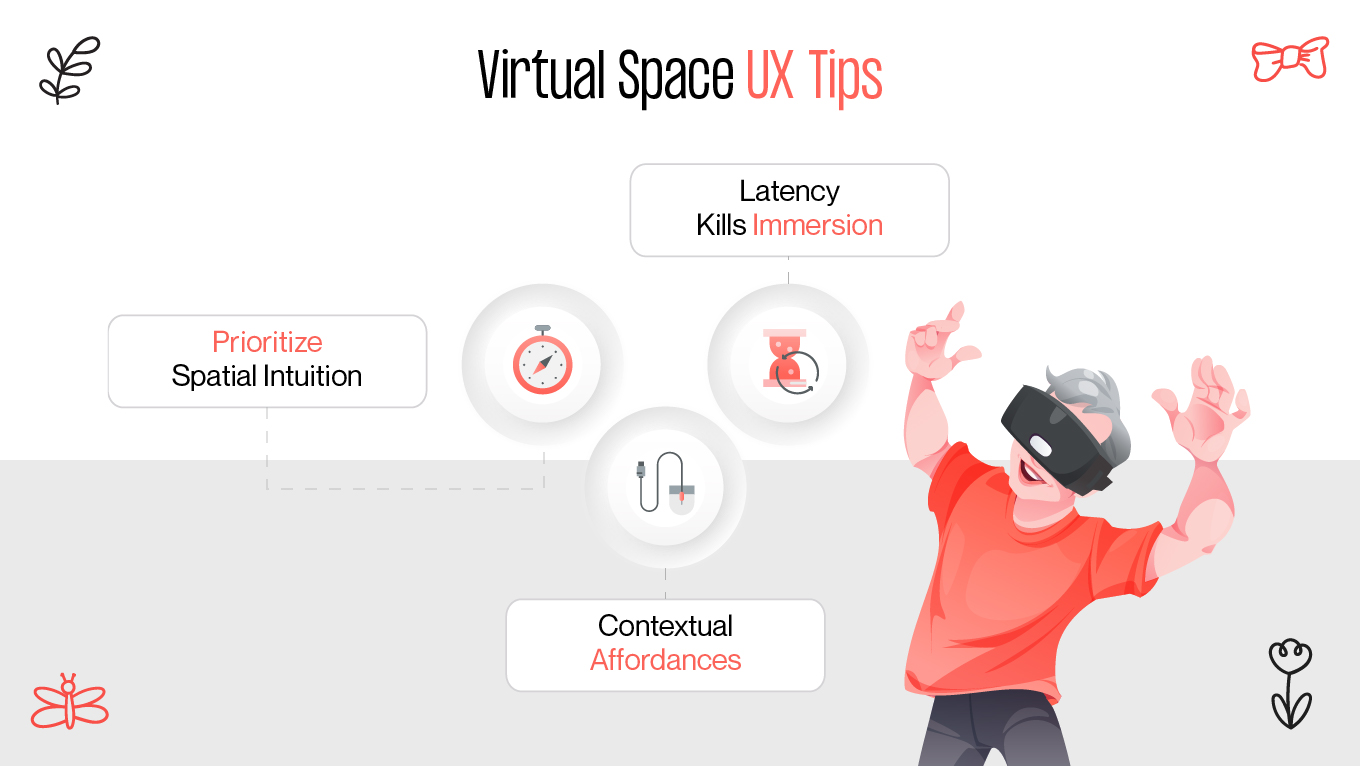
Virtual worlds are completely immersive and interactive, allowing users to engage with digital things and one another in a three-dimensional environment. The concept of the metaverse has evolved from a fictitious idea to one that is getting closer to becoming a reality thanks to technological advancements. With the increasing prevalence of this extended reality, UX design will play an increasingly significant role, and designers will undoubtedly encounter numerous difficulties in this novel setting. We should talk about it.