Designing a healthcare app sounds straightforward, until you remember that every tap, delay, and confusing screen can directly affect someone’s wellbeing. This is why 72% of health system executives say improving consumer experience, engagement, and trust is their top priority in 2025. The problem is that most digital healthcare products still overwhelm patients, frustrate clinicians, and fall short of accessibility and compliance expectations.
And when the experience breaks, the consequences are real: patients abandon portals, telemedicine visits go unfinished, clinicians revert to manual workflows, and trust erodes fast. The more complex the app, the more emotional and cognitive load it places on people who are already anxious or unwell.
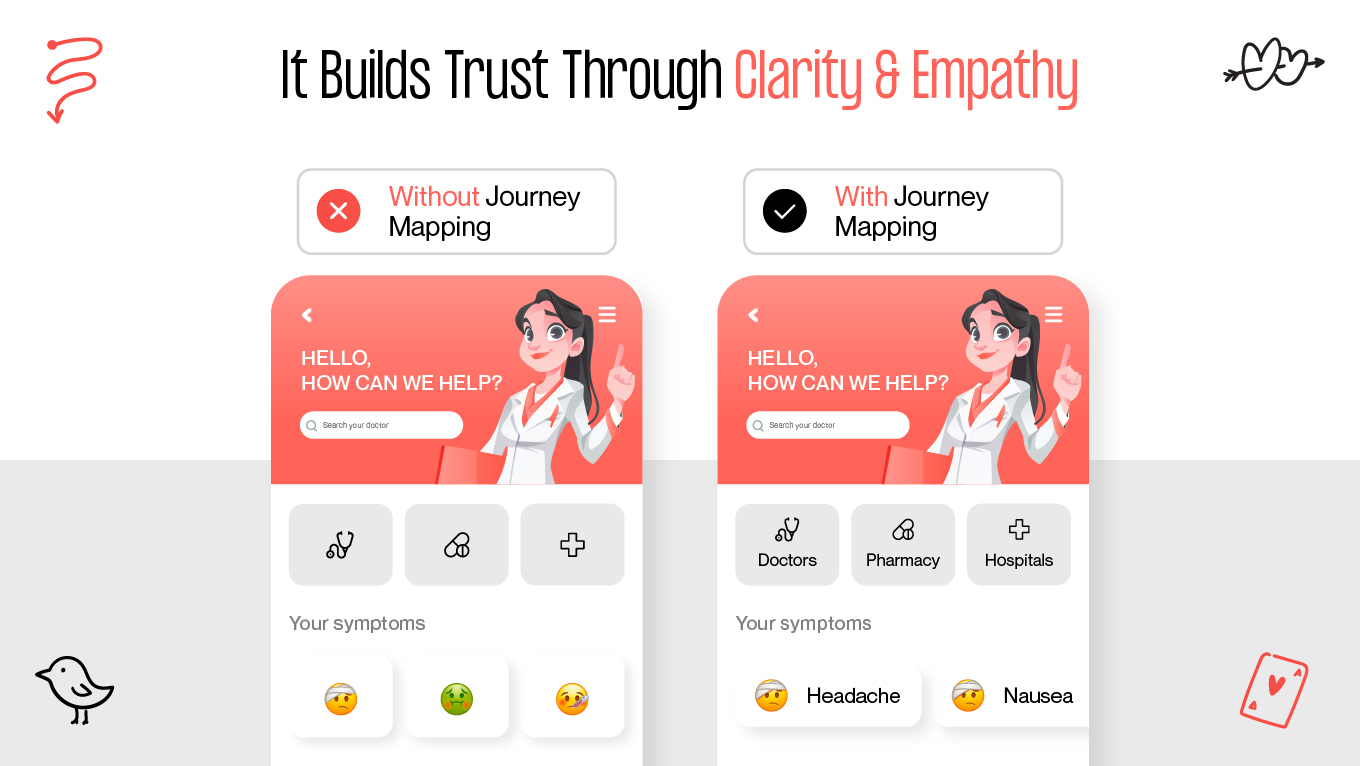
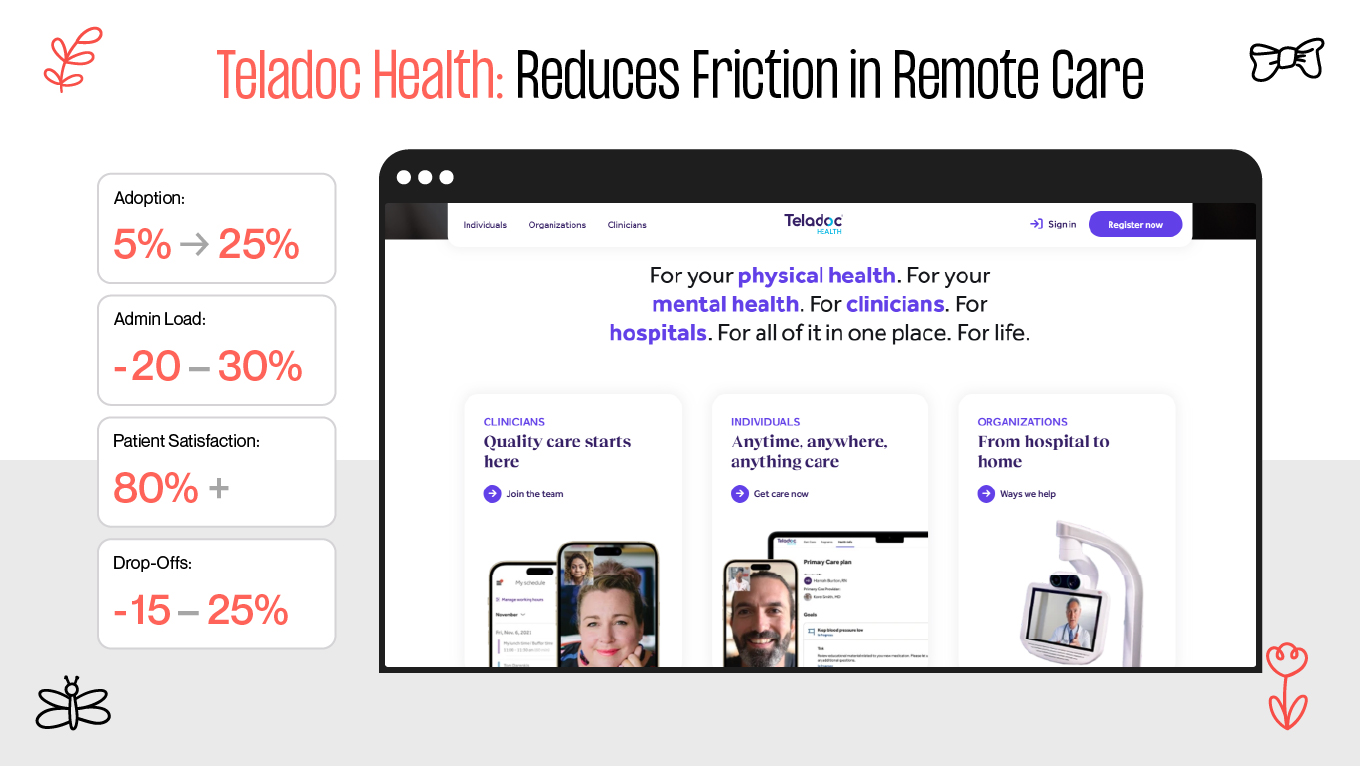
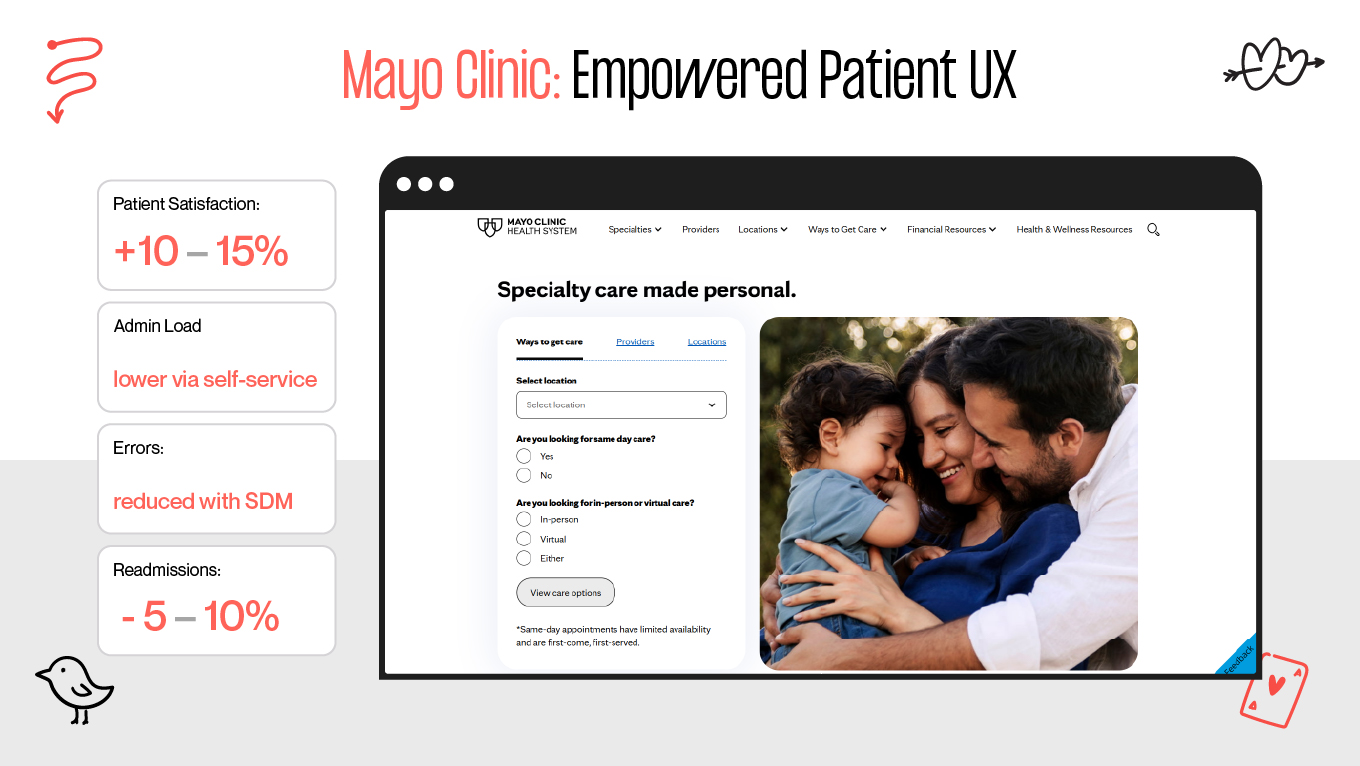
The way forward is shaping a healthcare app UX that anticipates stress, reduces friction, and prioritizes clarity, safety, and empathy at every step. In this guide, we’ll break down the unique challenges of healthcare UX and share practical design patterns and examples that help digital health products actually support the people who rely on them.