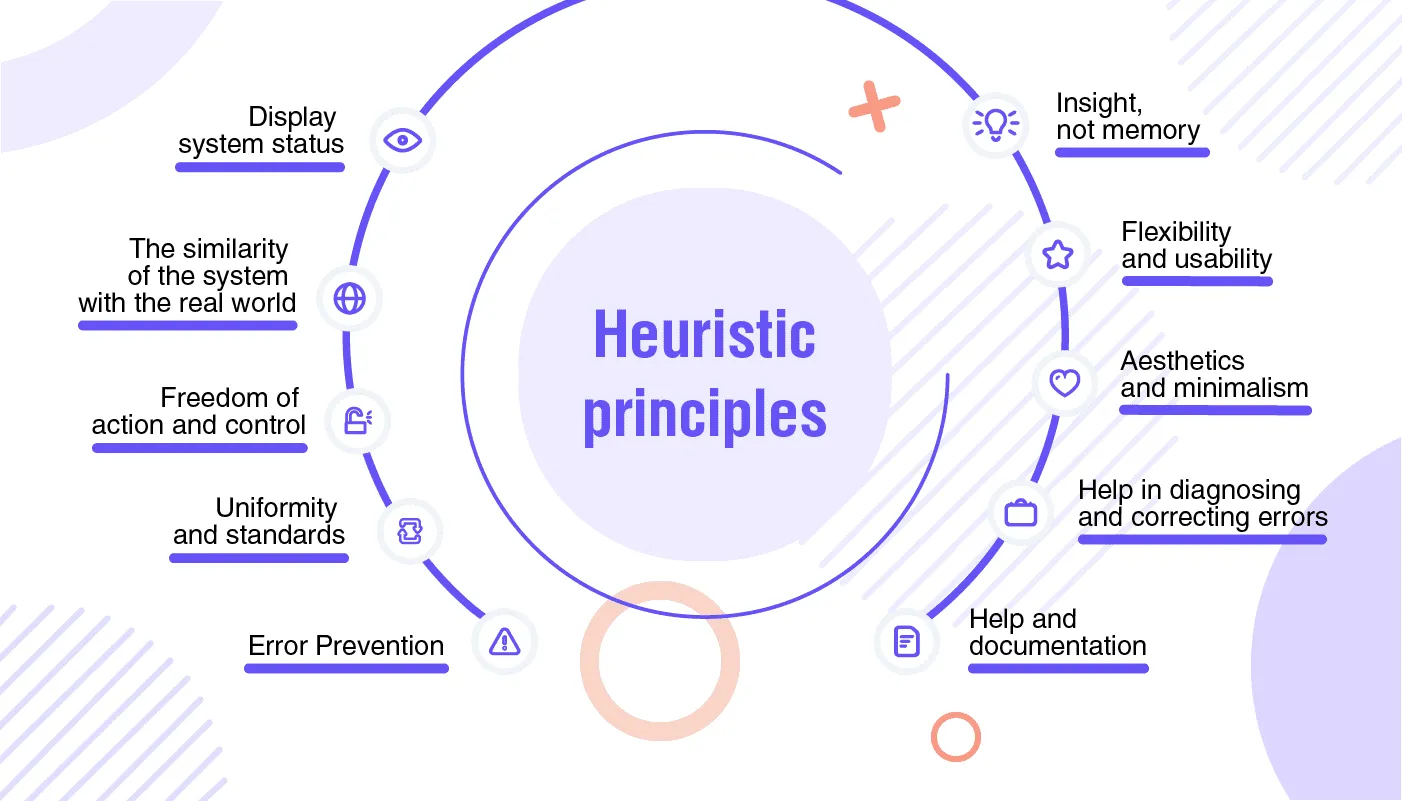
It’s no secret that a high-quality UX and UI design directly affects your potential customers’ satisfaction and income if your customers are pleased and purchase your product or services. Once your users’ expectations are not met, you get a low conversion rate and a high bounce rate. When facing such a problem, you need a UX audit to help you identify the problems and weaknesses of your website/application and find solutions.
In this article, we share our concise guide on how to conduct a UX audit in the right way and don’t let your app or website fail.