In the dynamic world of user experience (UX) design, understanding the user is not just a part of the process—it's the cornerstone. Did you know, for instance, that every dollar invested in UX results in a return of $100? Moreover, 88% of site visitors are less likely to return after a bad user experience.
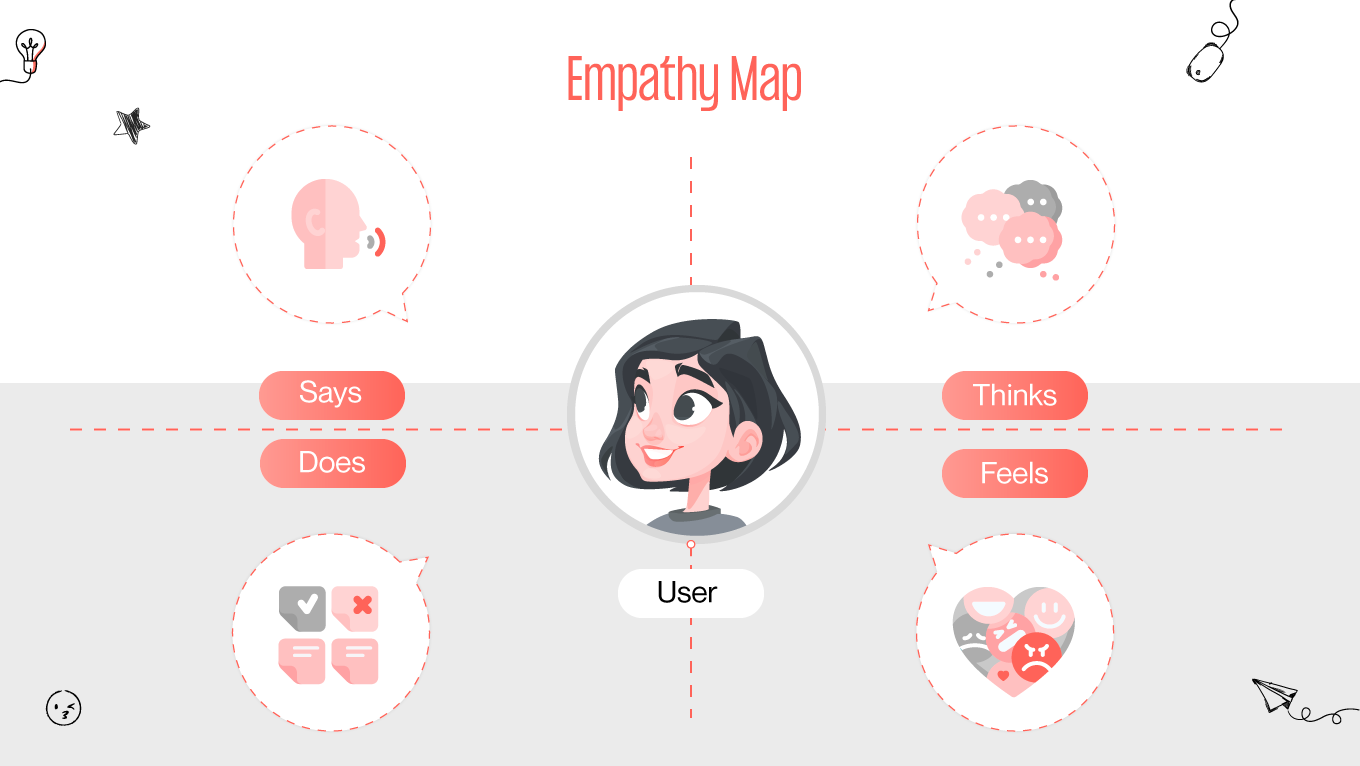
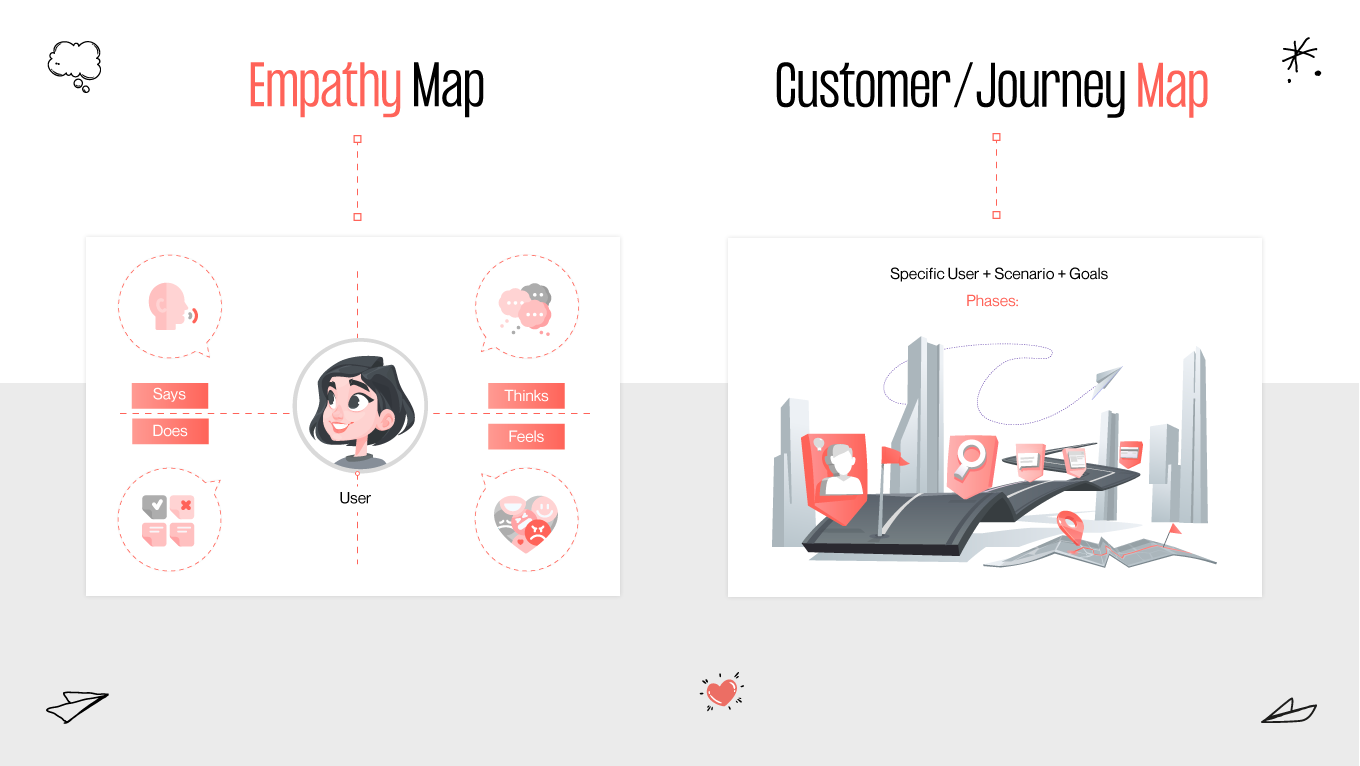
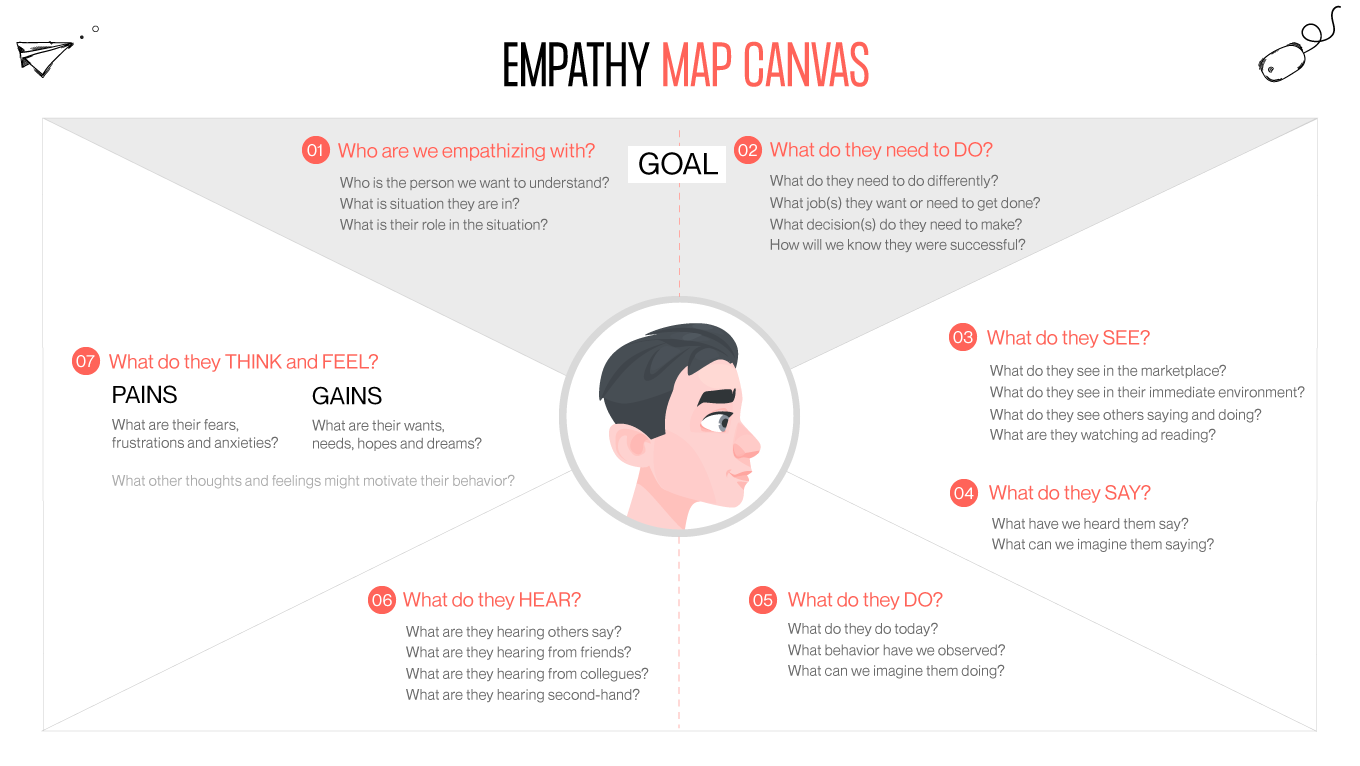
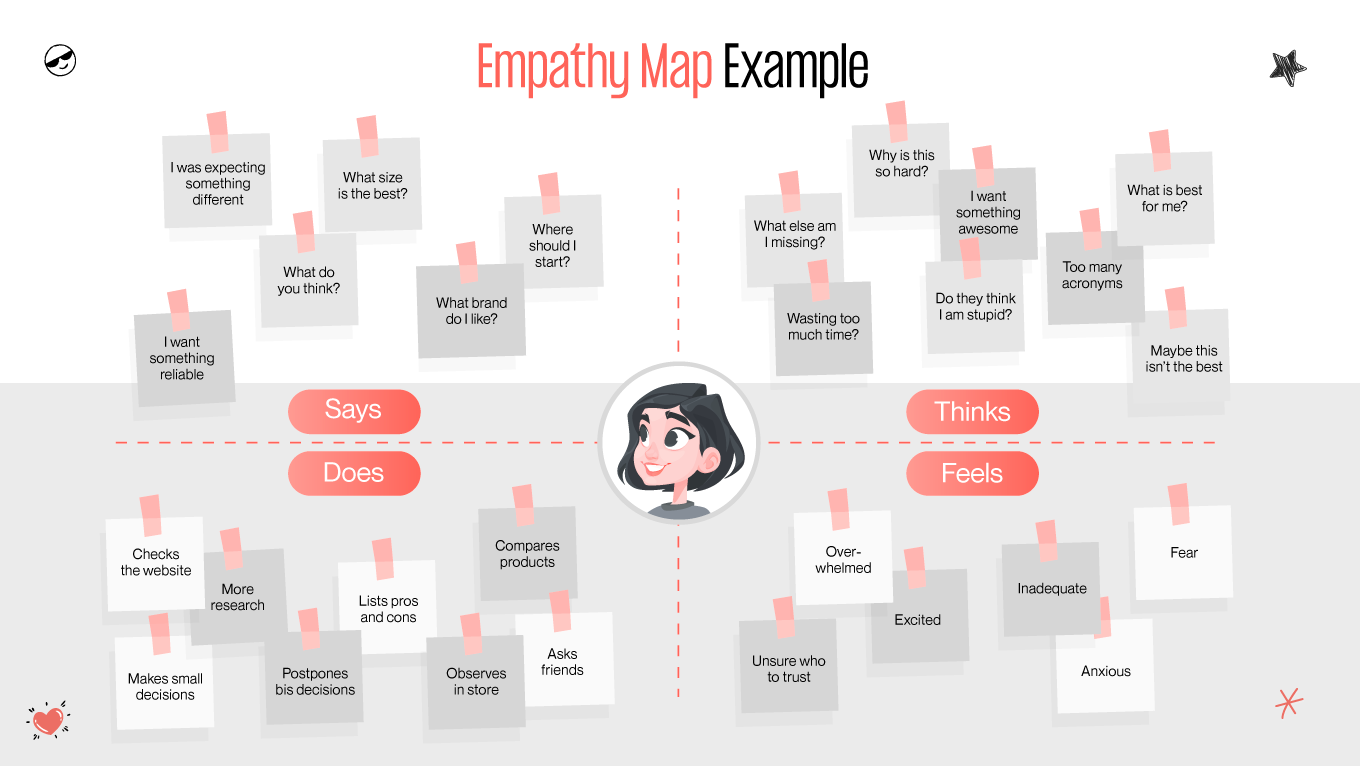
Gapsy Studio, a leader in innovative UX solutions, emphasizes the significance of this understanding through empathy mapping, a powerful tool that goes beyond traditional design approaches. Empathy mapping in UX design enables designers and stakeholders to step into the shoes of their users, gaining profound insights into their needs, experiences, and motivations.
This article delves into how empathy maps serve as a pivotal element in crafting user-centered designs, ensuring that every digital experience resonates deeply with its intended audience. Join us as we explore the transformative impact of empathy mapping on UX design, guided by the expertise and insights from Gapsy Studio.