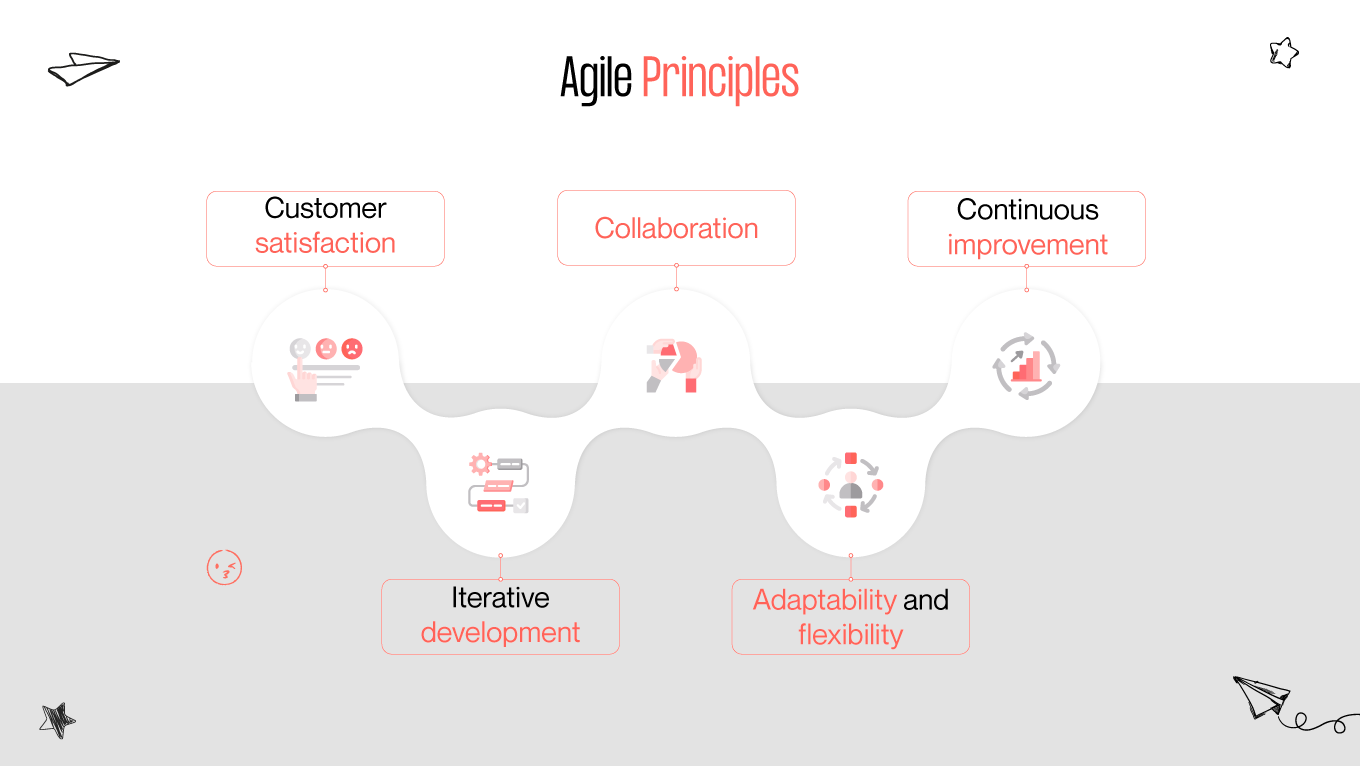
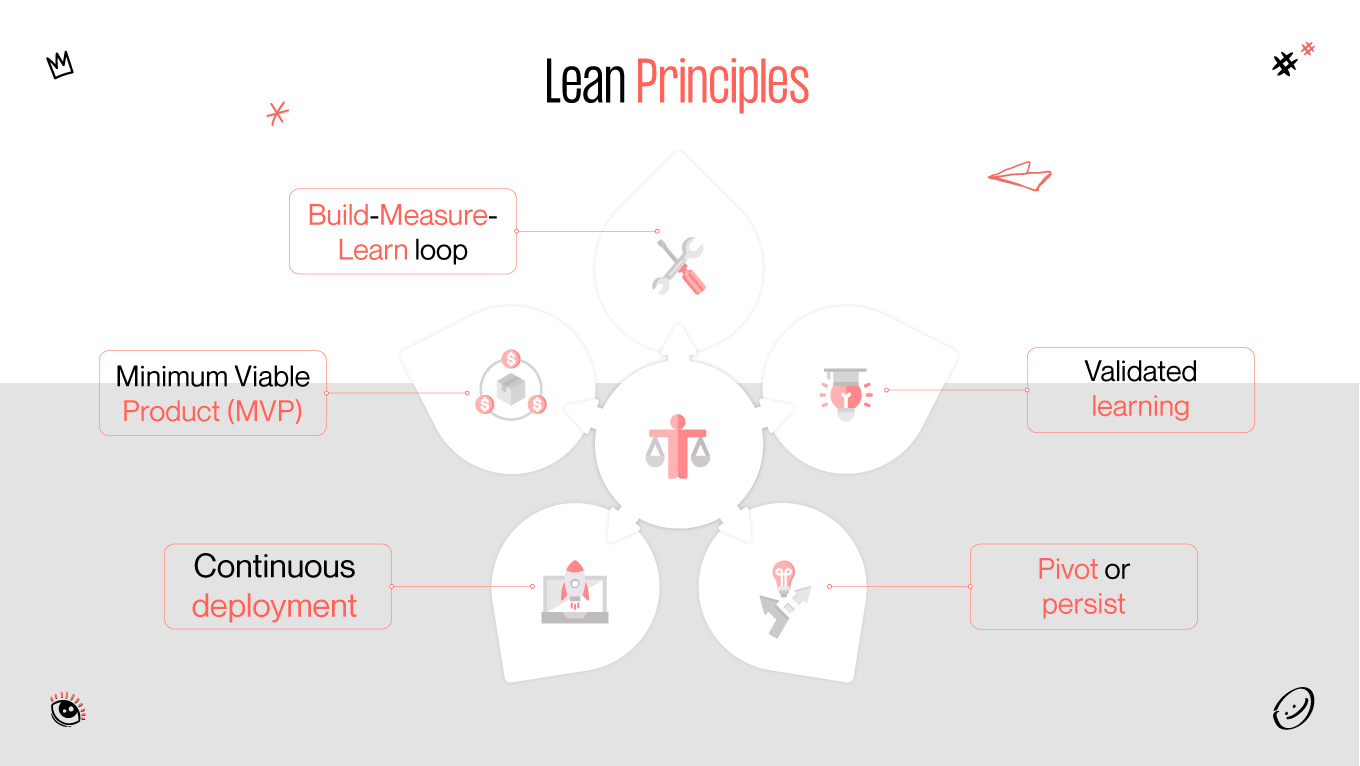
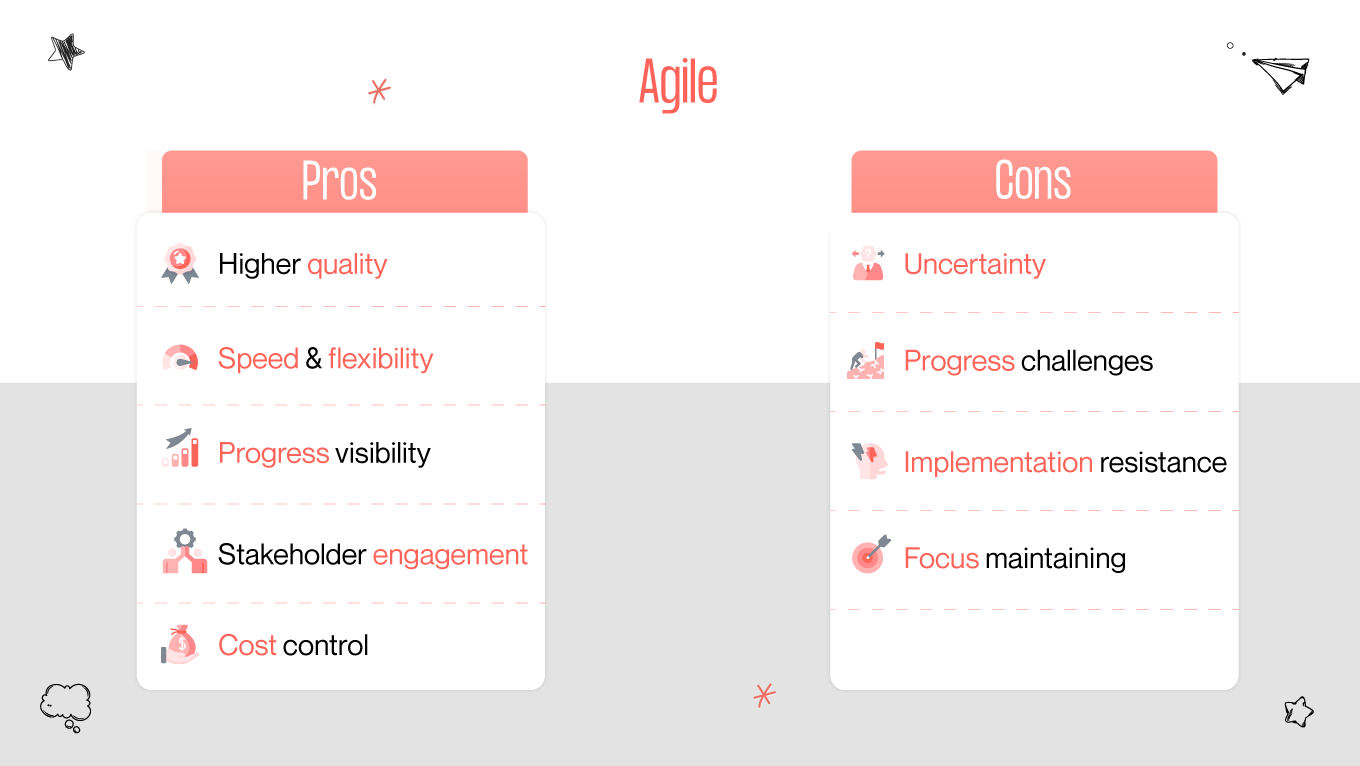
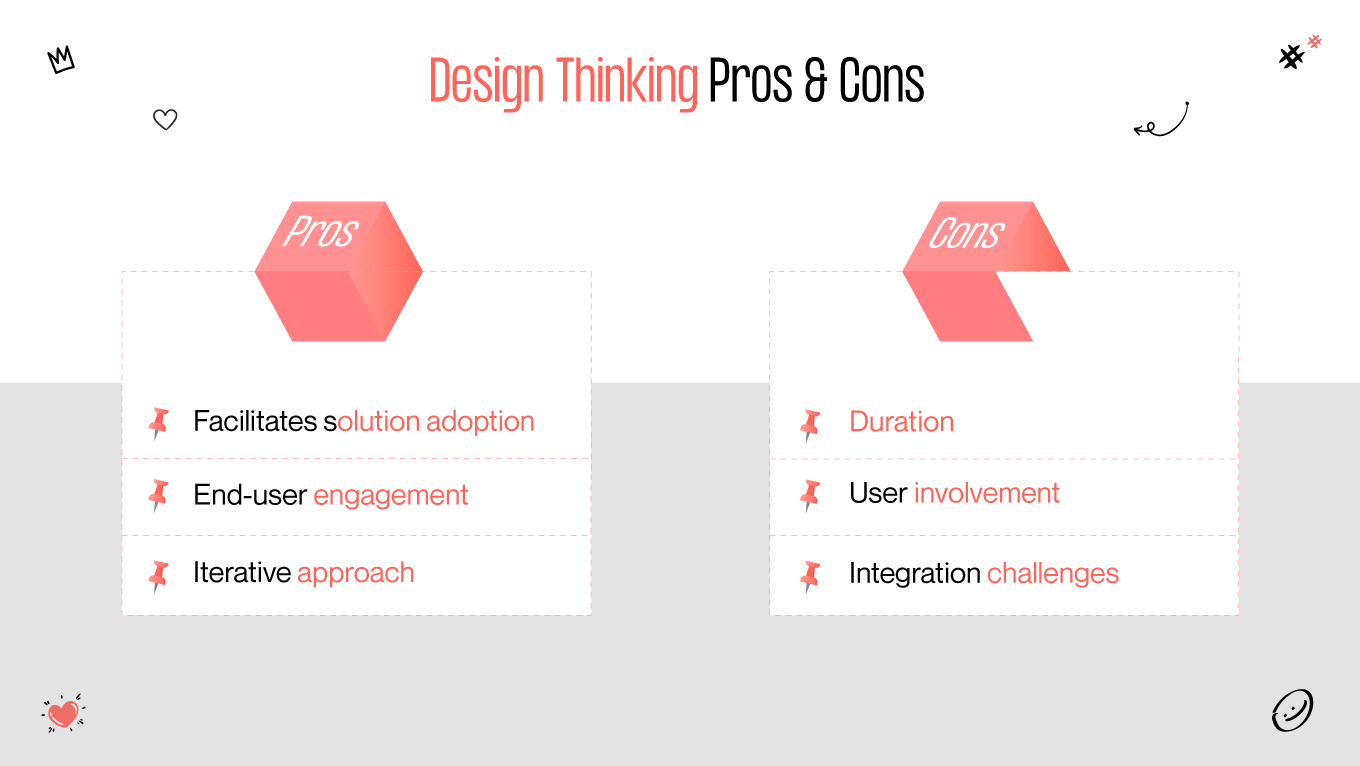
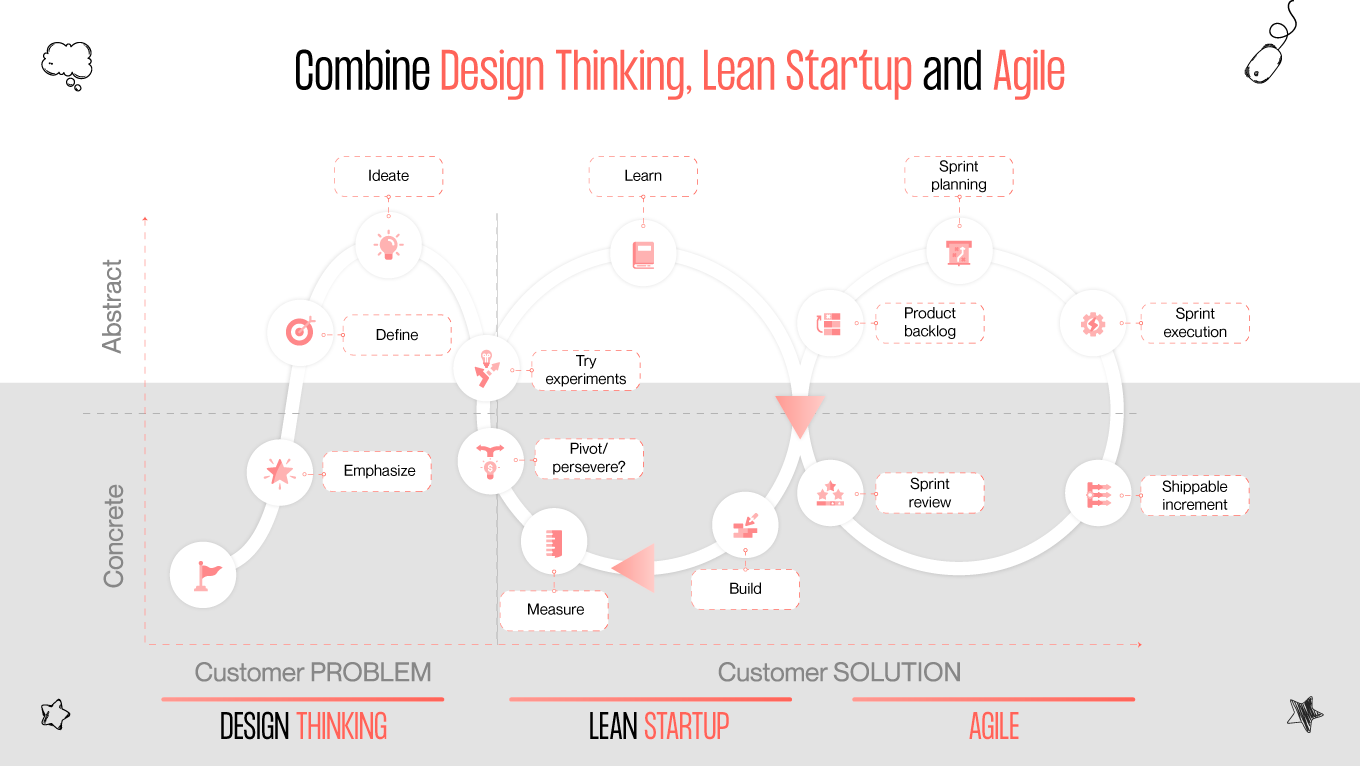
93% of Agile organizations reported better customer satisfaction, and 88% of people are unfamiliar with lean principles at all. In this era of rapid technological advancement and ever-evolving consumer demands, understanding the distinctions and synergies among methodologies such as design thinking, lean, and Agile is crucial for organizations striving to thrive in competitive environments. Each methodology offers unique perspectives, tools, and frameworks to streamline processes, enhance collaboration, and foster innovation.
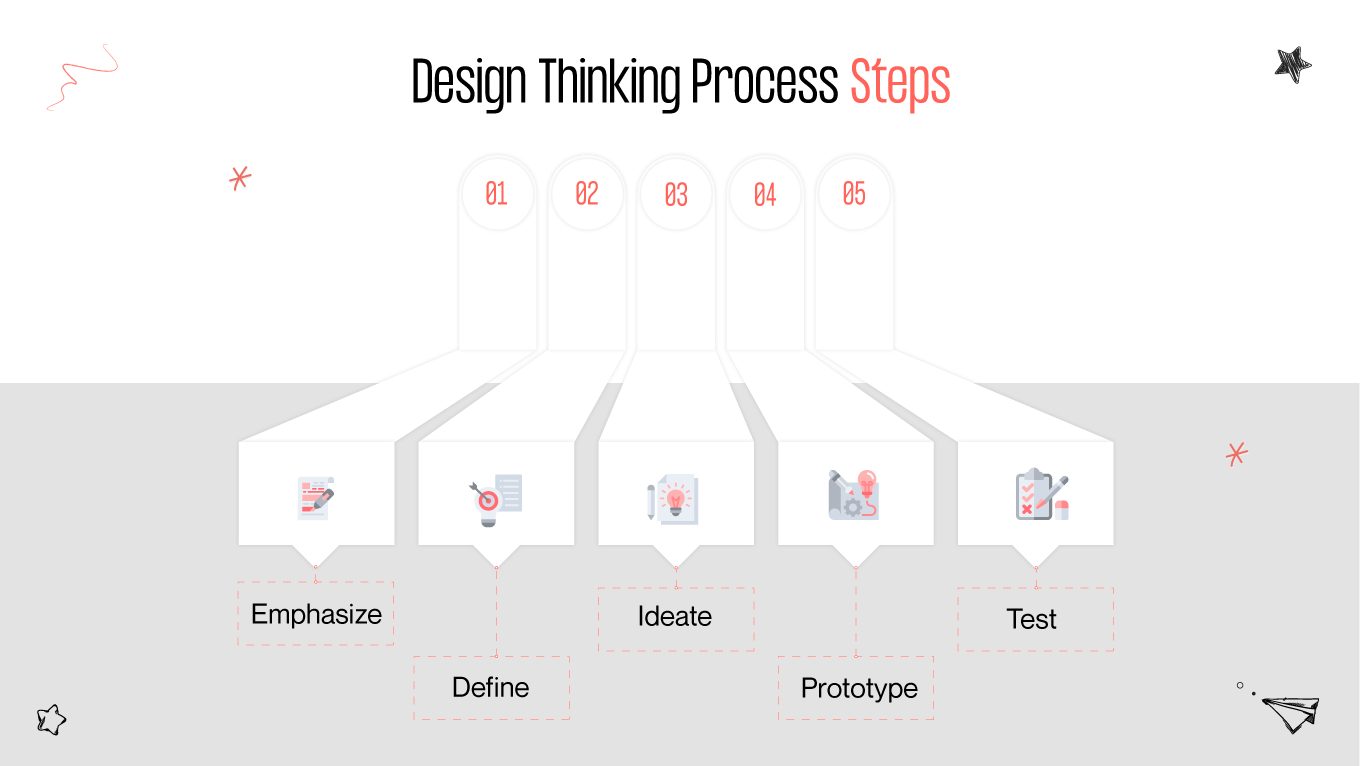
Do you know the difference between these three approaches? If not, join us to explore each one’s fundamental principles, key characteristics, and practical applications. Let’s uncover the transformative power they hold in shaping the future of business and innovation!