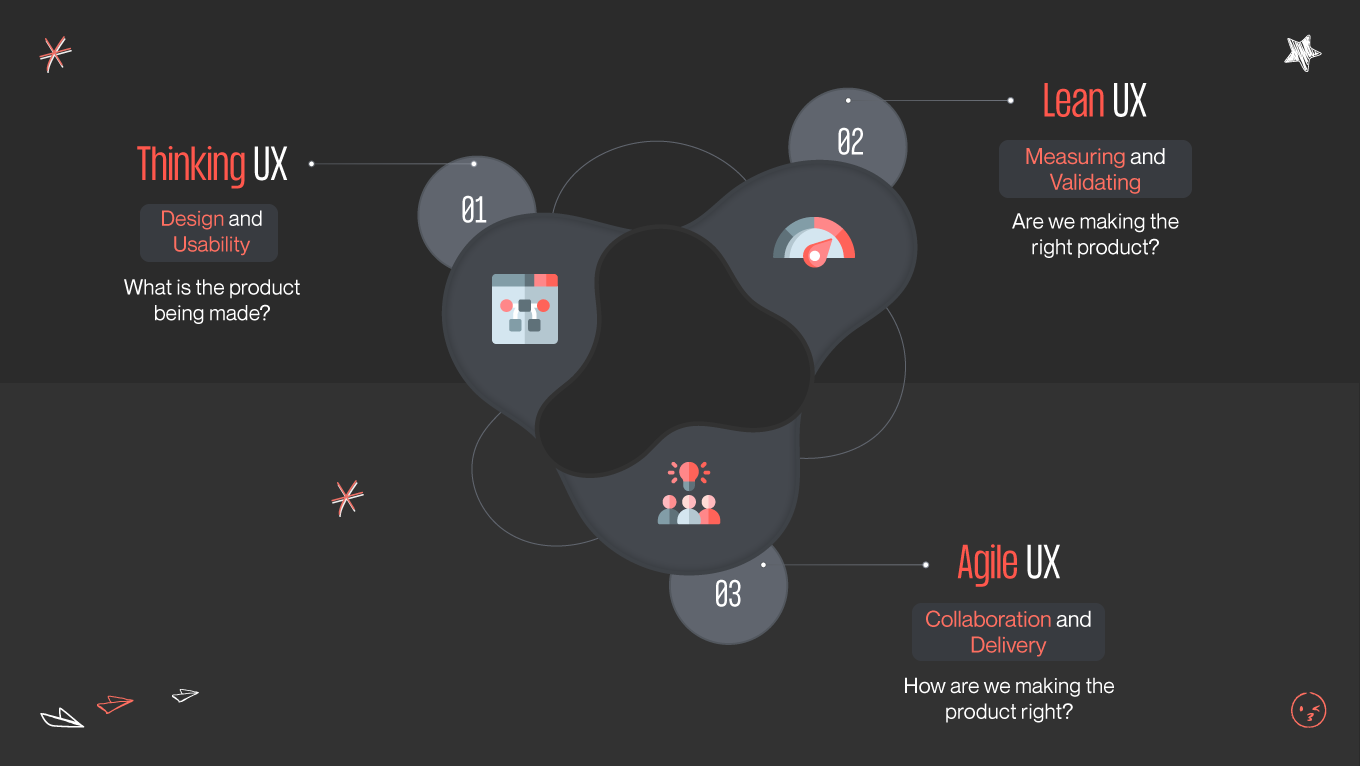
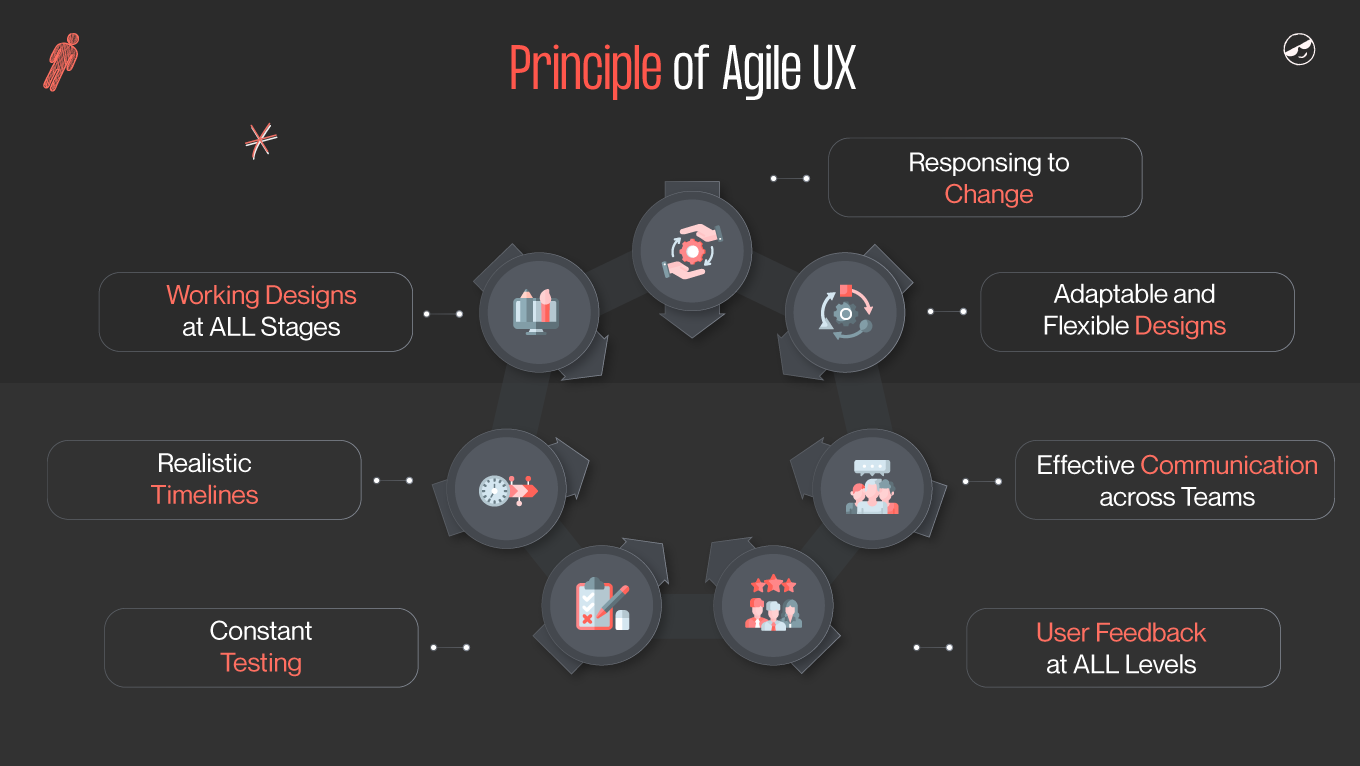
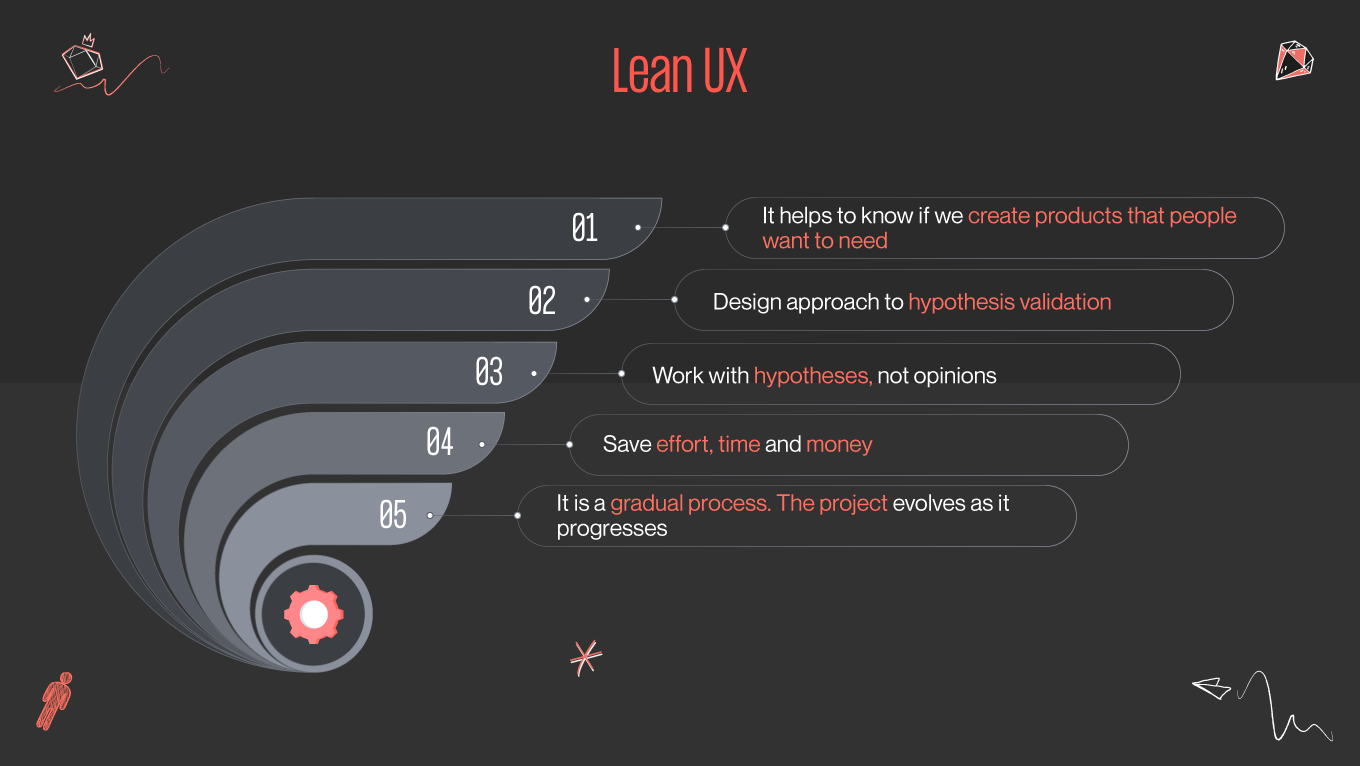
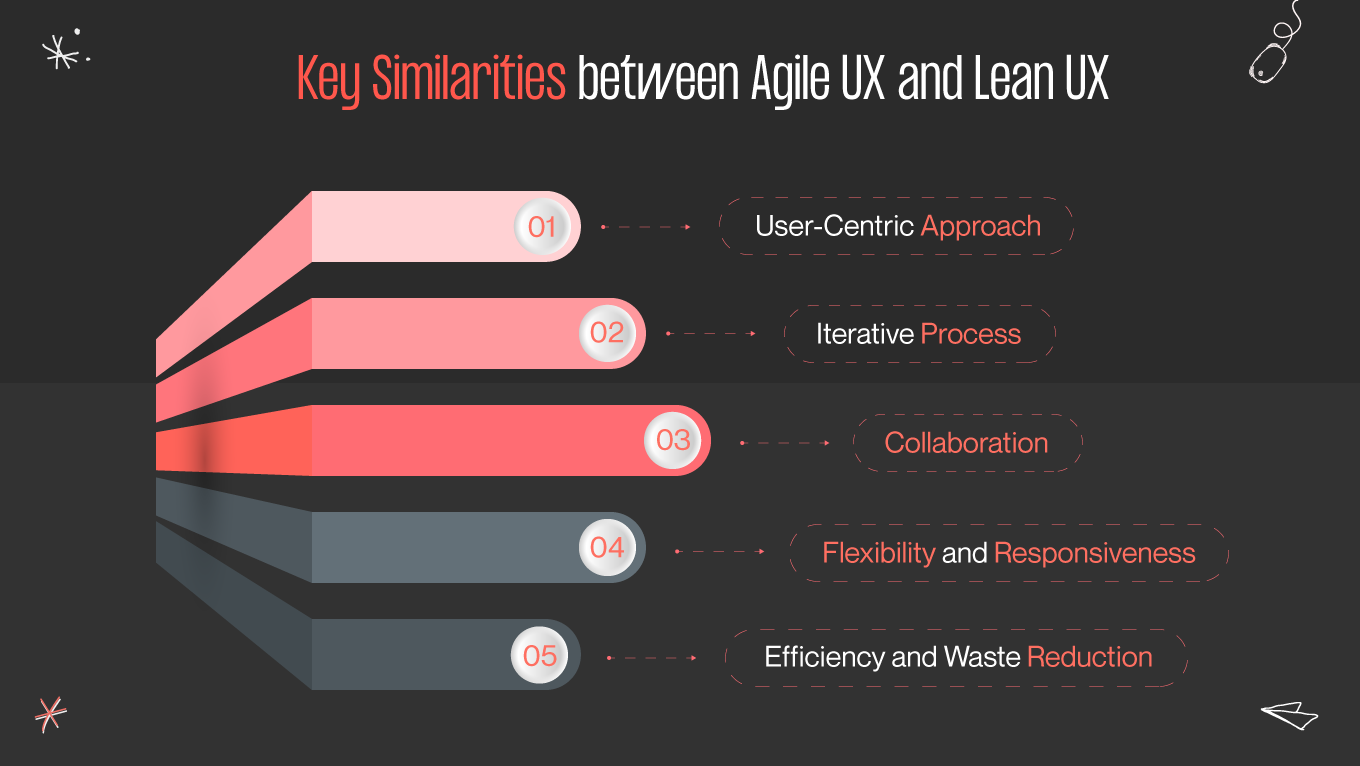
In user experience design, two methodologies have gained significant traction in recent years: Agile UX and Lean UX. Both approaches aim to streamline the design process and deliver user-centric solutions, but they have distinct characteristics that set them apart. In this article, we will delve into the principles, similarities, and differences between Agile UX and Lean UX, explore real-world case studies of successful implementations, discuss the challenges and limitations of each methodology, and examine how to integrate Agile UX and Lean UX for optimal results.