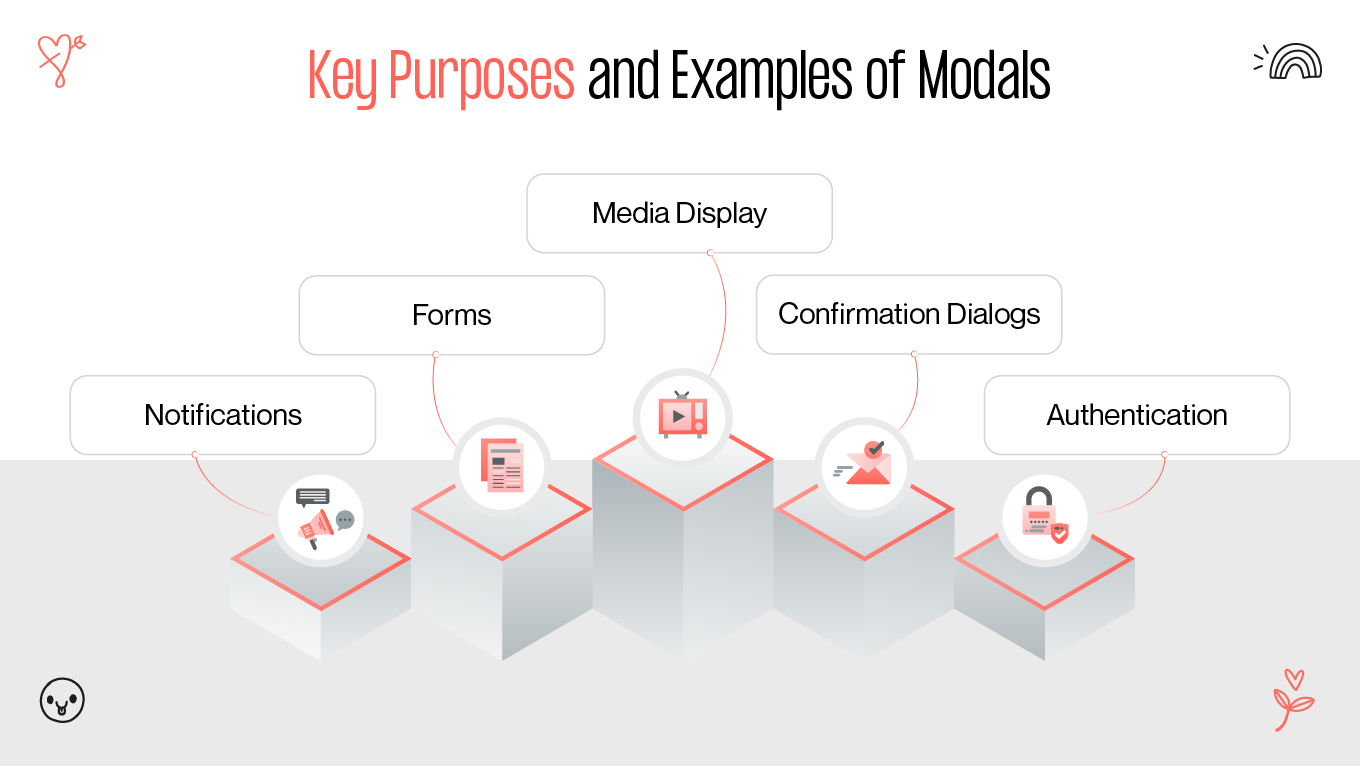
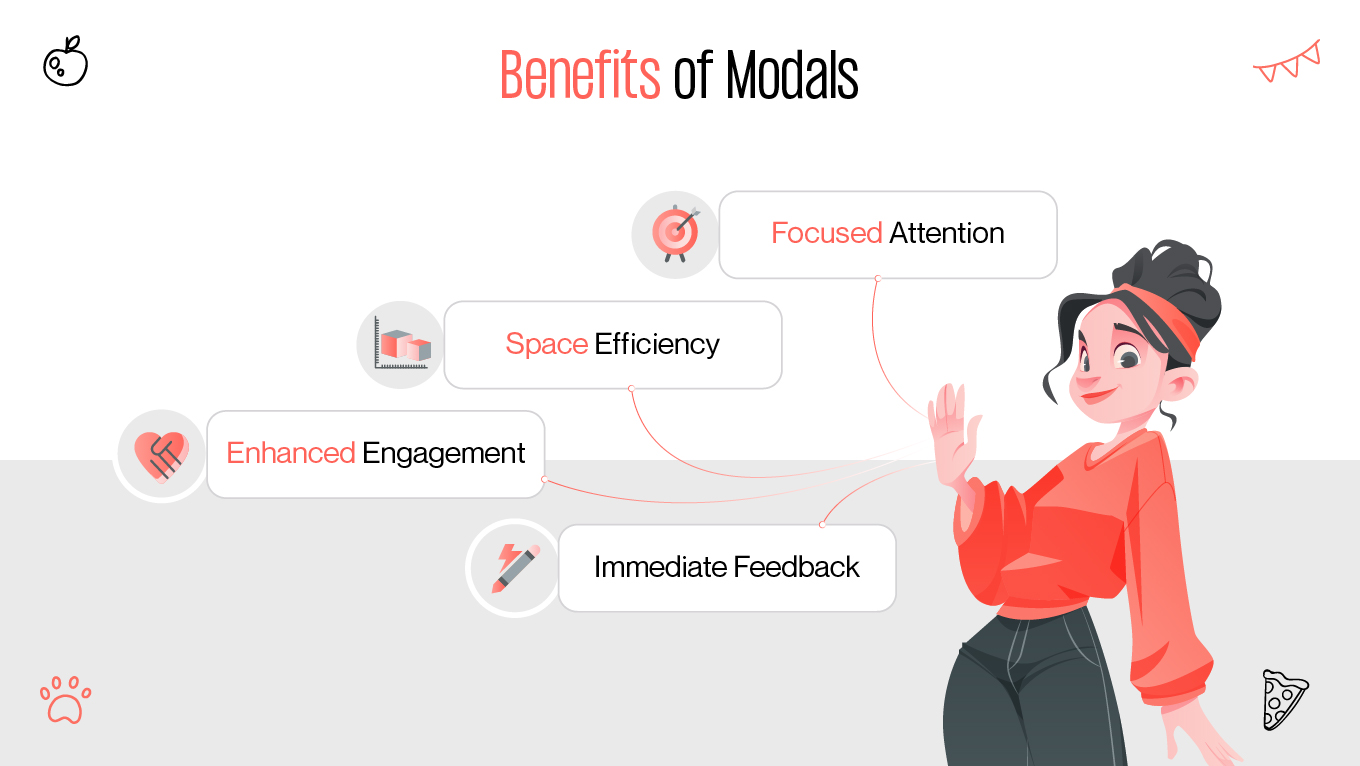
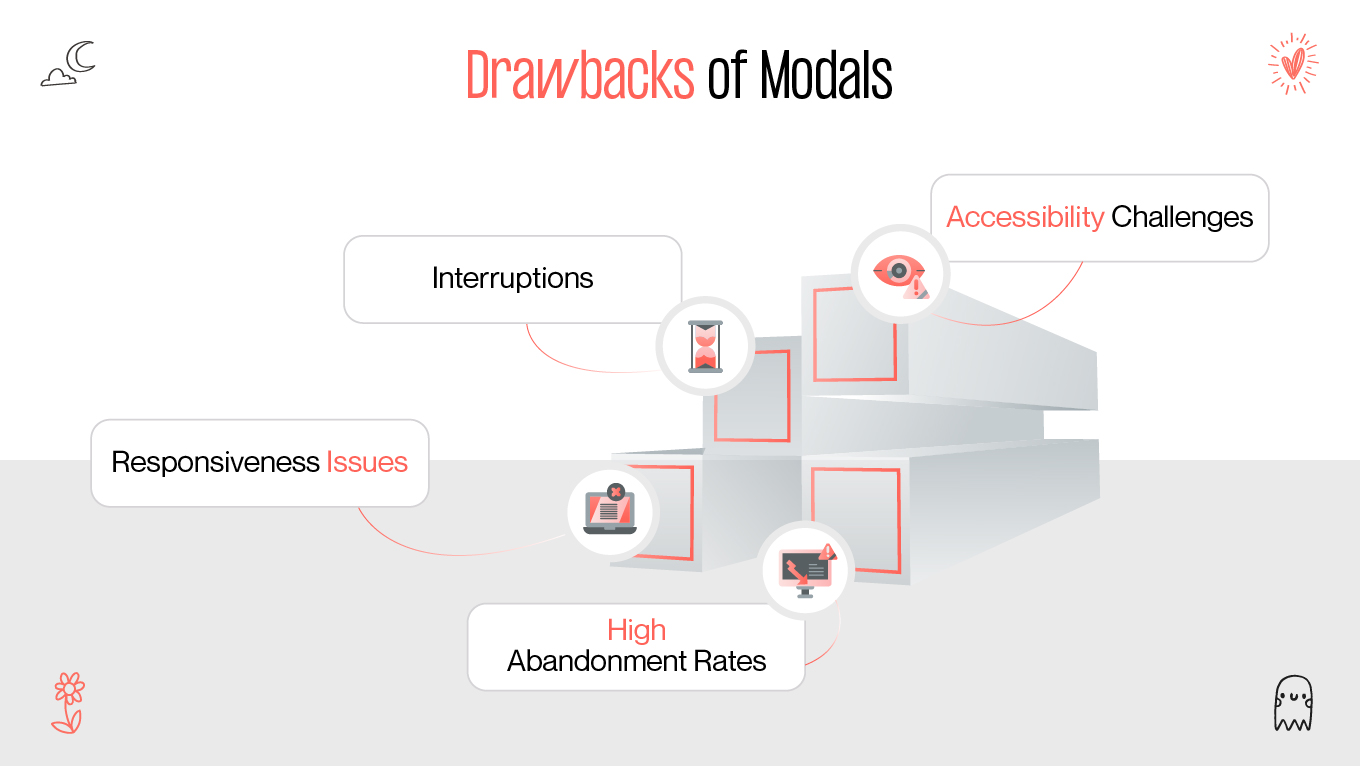
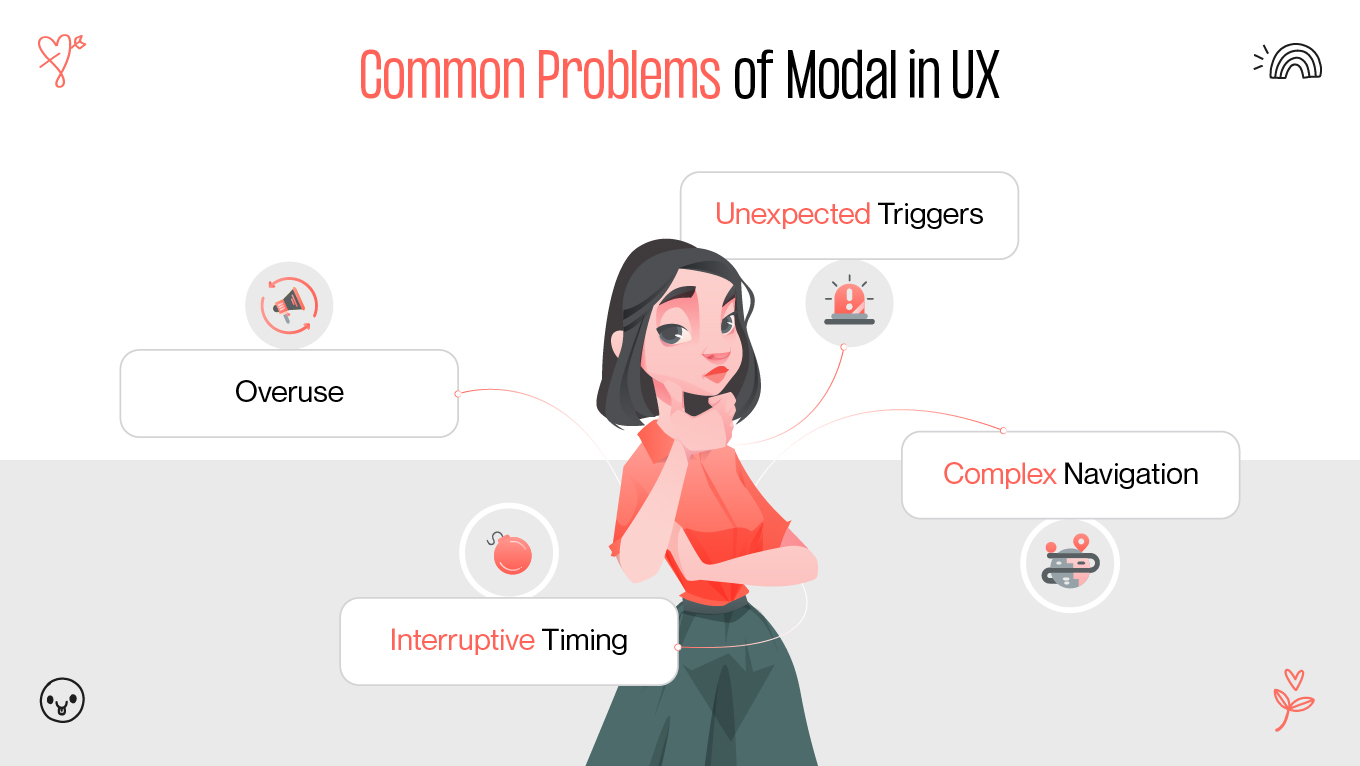
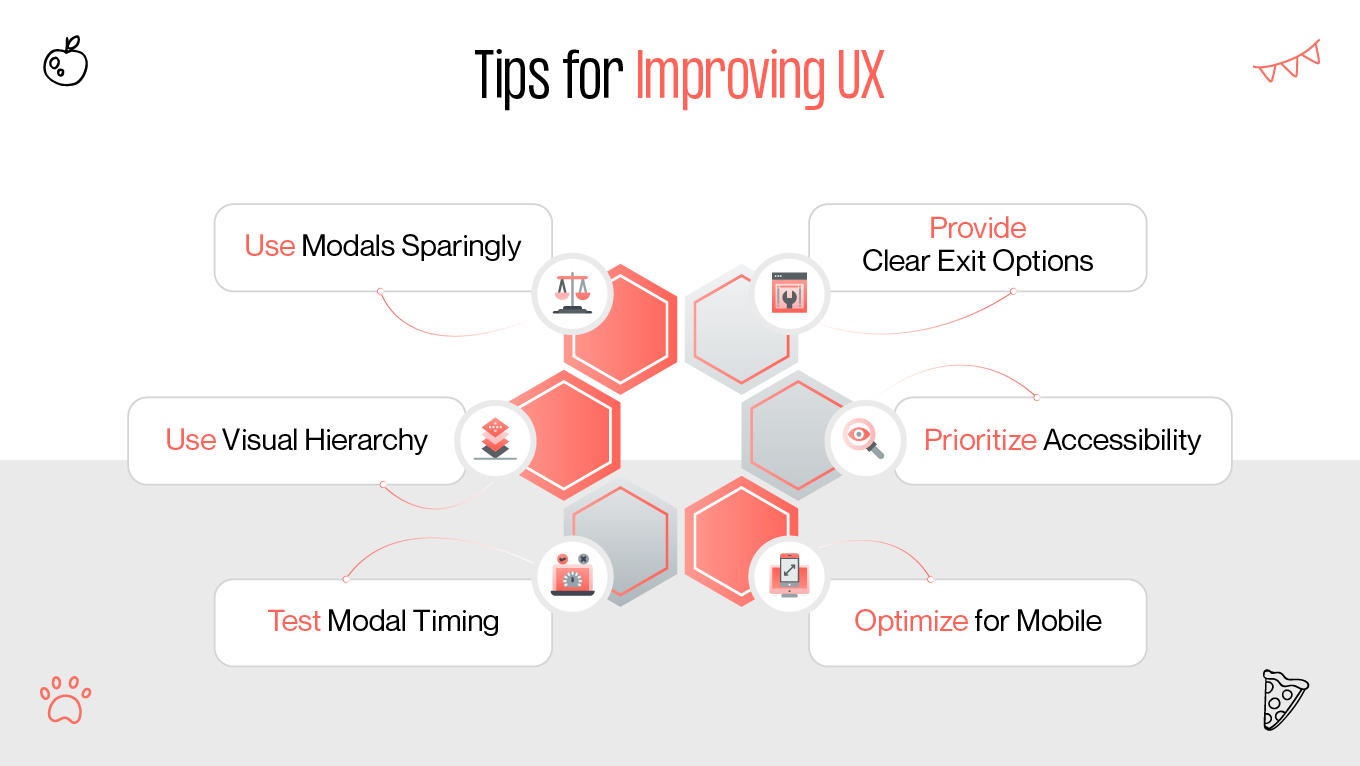
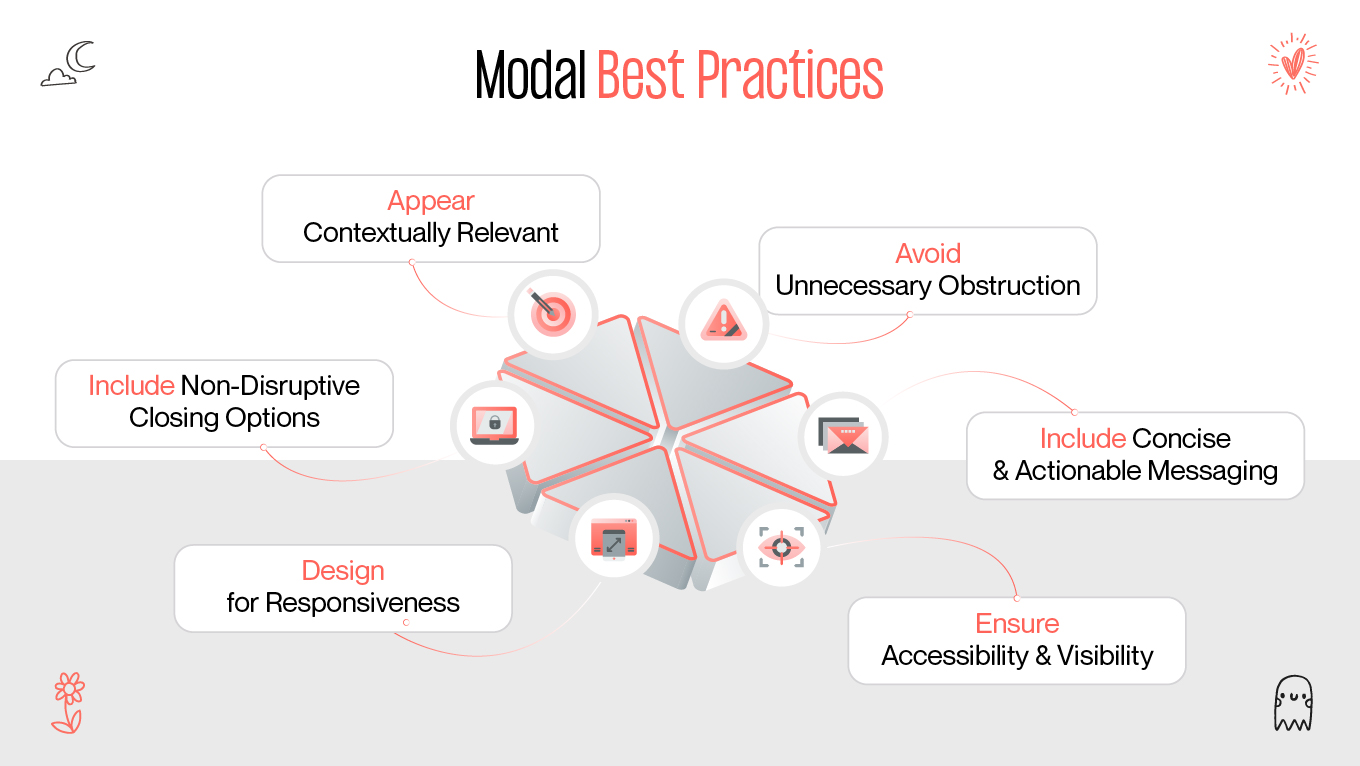
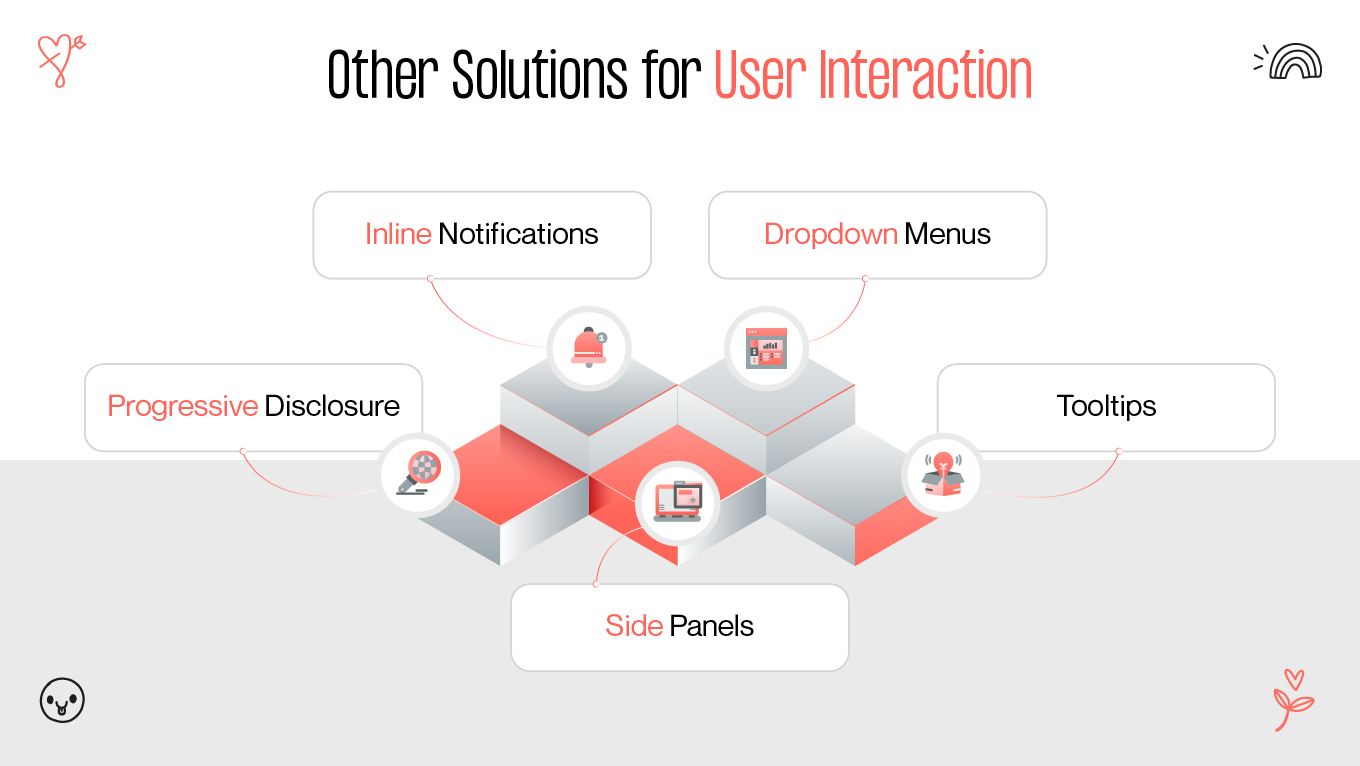
Modals are a ubiquitous feature in web design, but their impact on user experience (UX) remains a topic of debate. Some designers and developers laud modals for their ability to enhance usability, while others criticize them for interrupting user flow and causing frustration. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of modals, examining their purpose, advantages, drawbacks, and best practices to ensure they contribute positively to web design.