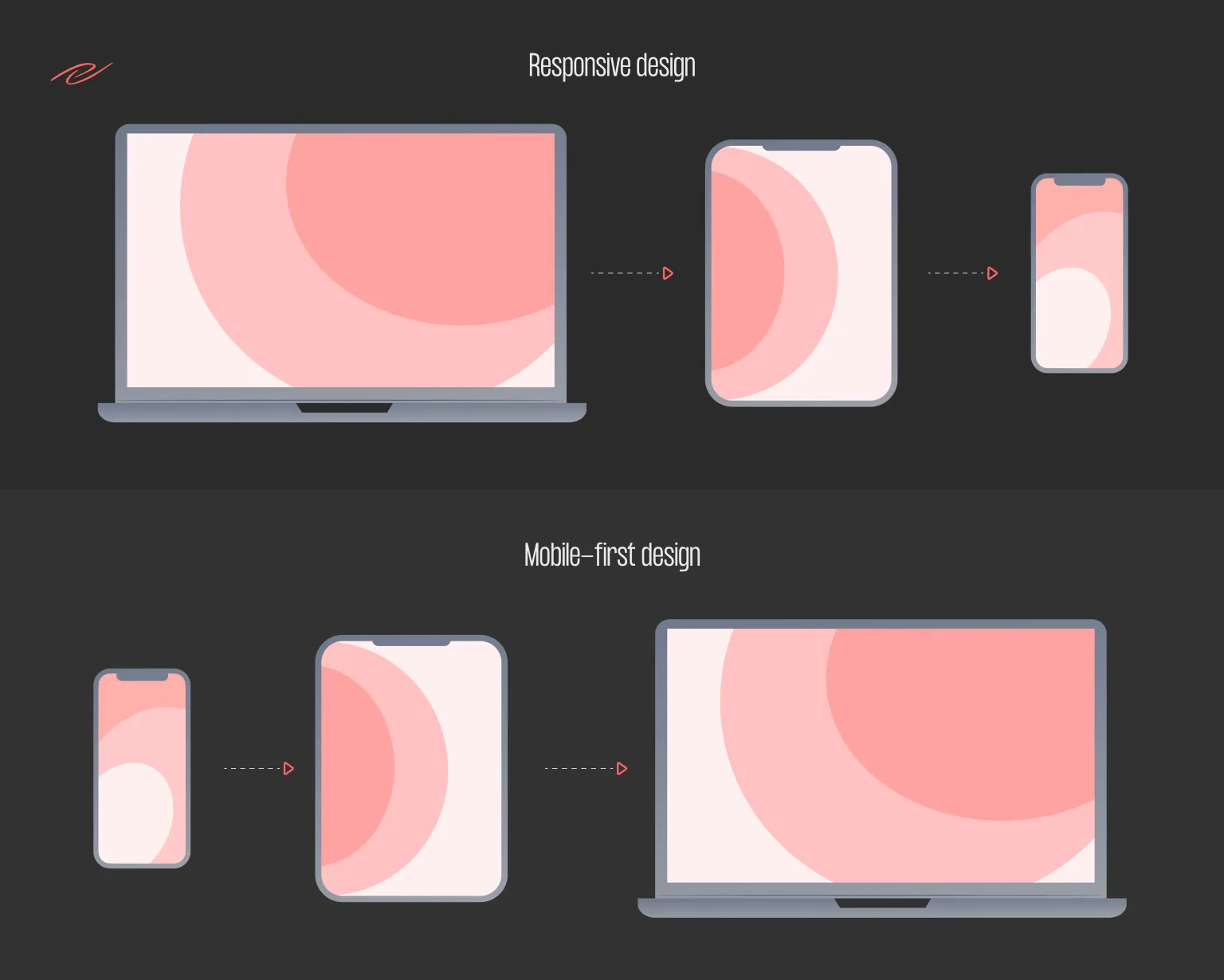
At the moment, half of all web traffic is from mobile sessions. In addition, more and more purchases are made using mobile devices – according to forecasts, by the end of 2021, the share of mobile commerce will be about 73% of all retail sales in e-commerce.
Such trends require more attention to the mobile version of the site – it should make the most positive impression on the user. Therefore, optimizing a site for various devices has long been one of the mandatory items in terms of reference for design. But what is the best approach to take for your smartphone- mobile-for оr responsive? In this article, we’ll cover the pros and cons, as well as the basic principles, benefits, and pitfalls of these two methods.